Why Tomato Plants Grow Leaves but Don’t Produce Fruit
It’s frustrating to see healthy green tomato plants with lots of leaves but no flowers or fruit. This common issue is usually caused by imbalanced nutrients, lack of sunlight, or environmental stress.
1. Too Much Nitrogen Fertilizer
Nitrogen promotes leafy growth. When tomato plants receive too much nitrogen:
- Leaves grow large and dark green
- Flowering is reduced
- Fruit production is delayed or stopped
Solution: Use a balanced or fruiting fertilizer with lower nitrogen and higher phosphorus and potassium.
2. Not Enough Sunlight
Tomato plants need at least 6–8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Without enough sun:
- Flowers may not form
- Existing flowers may drop
Solution: Move potted tomatoes to a sunnier location if possible.
3. Temperature Stress
Tomatoes struggle to set fruit when:
- Temperatures exceed 32°C (90°F)
- Night temperatures stay above 24°C (75°F)
Solution: Provide shade during extreme heat and water consistently.
4. Poor Pollination
Poor pollination is a common reason plants, especially fruiting plants like tomatoes, produce flowers but fail to set fruit. Pollination occurs when pollen is transferred from the flower’s male parts to the female parts. This process is often assisted by natural airflow, wind, or pollinating insects such as bees.
Challenges in enclosed spaces:
- Balconies, greenhouses, or areas with little air movement
- Pollen may not be released or transferred effectively
- Flowers drop without forming fruit
Common Solutions:
- Gently shaking or tapping the plant helps release and spread pollen
- Improving air circulation around plants supports natural pollination
- Planting flowers nearby can attract beneficial pollinators
- Reducing pesticide use protects pollinating insects
How Fertilizer Improves Tomato Fruit Production
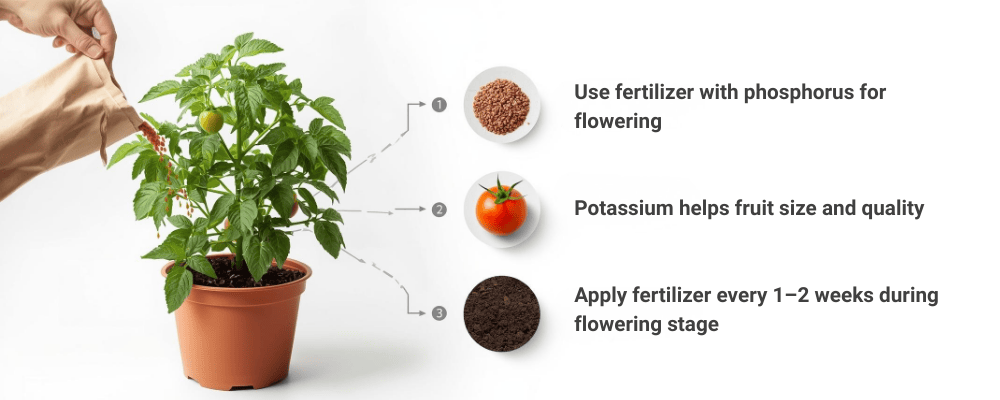
- Use fertilizer with phosphorus for flowering
- Potassium helps improve fruit size and quality
- Apply fertilizer every 1–2 weeks during the flowering stage

